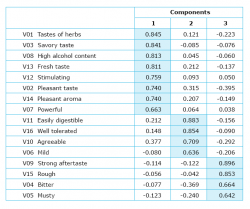
Factor Analysis
Objective of Factor Analysis
The objective of factor analysis is summarizing information, i.e. reducing the number of dimensions.
- Generating dimensions that are independent of one another, so that every dimension provides different information as compared to the others.
- Checking contents: Through the clustering of attributes, the meanings of the items to the respondents become clearer.
Classic definition: The objective of factor analysis is to determine the fundamental dimensions (ratings or attitudes) that lie behind the observed attributes.
Compared to conventional results, the presentation of factor values is more concise and easier to grasp.
The grouping of statements into baskets with homogeneous content clarifies the associations that lie behind these statements in the minds of respondents. (Often the real validity of the content is different from the meaning that had been assumed by the researcher).
Prerequisites
At least 50 to 60 cases should be incorporated into the analysis.
The method requires metric measurement values. However, it is fairly robust when faced with deviations from the normal distribution and from a pure interval scale. Because “yes/no” data can also be interpreted metrically, it can also be used to carry out factor analysis.
The attributes should be collected homogenously, if possible in a battery of statements that are queried using the same scale and introduced with identical instructions.