Regression Analysis
Objective of Regression Analysis
The goal of regression analysis is to answer the question: How is an attribute influenced by one or several other attributes?
The feature being influenced is typically an important general criterion which we would like to modify but which cannot be controlled directly. In order to nevertheless implement such a change, and to do it as effectively as possible, we must know which items strongly influence the attribute.
Compared to cross tabulation for uncovering interrelationships, the regression analysis provides:
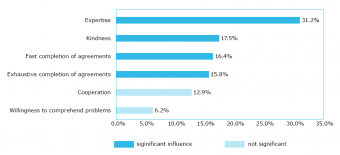
- Directly comparable characteristic values for the magnitude of the influences (weights).
- Information on the total size of the degree of explanation through the influencing attributes (multiple correlation coefficient, coefficient of determination).
- Information on the degree of statistical confidence of the results (significance level).
Prerequisites
At least 50 to 60 cases should be included in the analysis.
The method requires metric measurement values. However, it is fairly robust when faced with deviations from the normal distribution and from a pure interval scale level. Because “yes/no” data can also be interpreted metrically, it can also be used to perform a regression analysis.
The influence variables should be largely independent from each another.
The design of the model is important:
- The direction of influence must be unambiguous.
- The interrelationship between the influenced variable and each influencing variable should be linear.